Coenzyme Q10 – Uses, Benefits, Sources and Dosage
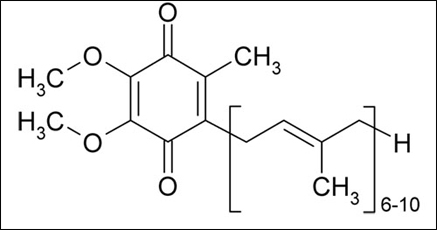
Coenzyme Q10 is a vital catalyst – the spark plug for the conversion of food to energy within the cells. It is also an important nutrient and found in the every plant and animal cell. It is the powerful antioxidant thus prevents the cellular damage in the body. It helps to improve the energy production in the body. Moreover Coenzyme Q10 releases the 95% of energy required for the life and its deficiency results in the fatigue, hypertension and several other complications. Coenzyme Q10 is present in herb Arjuna and offers the cardio protective properties.
Benefits of Coenzyme Q10
- It helps in the energy production for the healthy growth and functioning of cells.
- It helps to reduce the high cholesterol levels.
- It lowers the high blood pressure levels.
- It maintains the healthy blood sugar levels thus good for diabetes.
- It helps in cancer prevention and recurrence because of its antioxidant activity.
- It has been found that people who have taken the daily CoQ10 supplements within the 3 days of heart attack were less prone to the later chest pain and heart attacks.
- It helps to slow down the early muscular degeneration.
- It also prevents attack of migraine.
- It reduces side effects of chemotherapy.
- It is also used in the treatment of kidney failure.
- It is good for the heart related complications like angina, arrhythmia, heart attack, clogged heart arteries and congestive heart failure.
- It helps to provide relief in the chronic fatigue.
- It is good for allergies and asthma.
- It improves the sperm motility hence good to improve the male fertility.
- It Improves the immunity in the people who have HIV or AIDS.
- It is good for yeast infections like candidiasis.
Food Sources of Coenzyme Q10
- Meat – Pork heart, beef heart and reindeer meat contains the highest amounts of coenzyme Q10. Other meat products which are also packed with coenzyme Q10 may include beef, pork, beef liver and pork liver
- Oils – Sesame, Soybean, corn oils and cottonseed have good amounts of coenzyme Q10.
- Fish – Cuttlefish, Sardine, mackerel, yellow tail, tuna Pollock and herring are packed with moderate to high amounts of coenzyme Q10.
- Nuts, Beans and Seeds – Peanuts, Soybeans, sesame seeds, pistachios, walnuts, hazelnuts and azuki beans contain good amounts of coenzyme Q10.
- Vegetables – Broccoli, spinach, sweet potato, sweet pepper, garlic, peas, carrots and cauliflower also contain the significant amounts of Coenzyme Q10.
Deficiency of Coenzyme Q10
- Coenzyme Q10 is important for energy production. Deficiency of Coenzyme Q10 may result in the extreme physical fatigue, muscle or joint pains, headache, migraine and mental fatigue.
- Coenzyme Q10 deficiency results in the low immunity and increases the susceptibility to infections.
- Reduced levels of Coenzyme Q10 causes the elevated cholesterol and blood pressure levels which increase the risk to heart complications.
- Reduced levels of Coenzyme Q10 also leads to the neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders.
Side Effects of High Intake of Coenzyme Q10
There are no serious side effects those have been found from the use of Coenzyme Q10. Rashes, nausea and upper abdominal pain and mild insomnia are the problems which can be associated with side effects of Coenzyme Q10. Other symptoms may also include heartburn, headache, fatigue and dizziness.




1 thought on “Coenzyme Q10”