Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis
Introduction
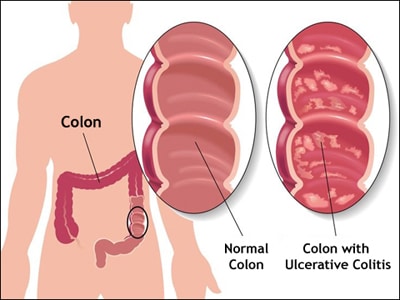
Ulcerative colitis is the chronic inflammation of the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon). It ranges from mild to severe.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The specific cause of ulcerative colitis is not known, but the probable cause of UC is improper functioning of the immune system. The other factors that may cause ulcerative colitis are hereditary, age and environmental factors.
Signs and Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
- Blood & mucus in stools
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Rectal pain
- Fatigue
- Increased abdominal sounds
- Gas formation
- Weight loss
- Lack of appetite
- Fever
Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is diagnosed by detecting the causes of signs and symptoms, a patient has. There are various tests and procedures that are used to confirm the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis.
Some other symptoms may develop when other parts of the body also get affected by ulcerative colitis:
- Pain and swelling in joints
- Skin problems
- Mouth sores
- Eye inflammation
Tests and Procedures Used to Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis
1. Endoscopy
In endoscopy, a small, flexible tube with a bright camera inside the top of the tube is inserted in the patient, which enables the doctor to examine the different parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The different endoscopy tests are the following:-
A. Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is one of the main endoscopy exams, which is commonly recommended by the doctor for diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. It is used to identify the alterations or abnormalities in the rectum and large intestine (colon).
In a colonoscopy examination, a flexible long tube named colonoscope is implanted into the rectum. There is a small video camera is at the top of the tube, which enables the doctor to see the inside of the entire large intestine. Colonoscopy is used to:-
- Examine the internal possible causes for intestinal symptoms such as rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, chronic constipation, chronic diarrhea, and other intestinal difficulties.
- Screening of colon cancer
- Examination of reoccurrence of polyps. If the patient had polyps previously them doctor may suggest for colonoscopy to investigate polyps. For this tissue samples can also be taken during a colonoscopy.
B. Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
This is also one of the main endoscopy exams, which is recommended by doctors for judging UC. It is used to examine the lower part of the large intestine.
In the flexible sigmoidoscopy examination, a slender, flexible tube named sigmoid scope is inserted into the rectum and sigmoid.
A small video camera at the top of the tube enables the doctor to observe the internal symptoms of the rectum and most often of the sigmoid colon. This endoscopy does not give a view of the entire colon. Flexible sigmoidoscopy exam is used to:-
- Examine the cause of intestinal signs and symptoms such as abdominal pain, alterations in bowel habits, rectal bleeding, chronic diarrhea, and other intestinal difficulties.
- Screening of colon cancer: It is one of the options for cancer screening but it does not give the view of the whole colon.
C. Other Endoscopy Examination which Helps to Diagnose UC
- Capsule endoscopy
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Double-balloon endoscopy
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests are recommended by the doctor for the patient of UC. The blood test is not enough to diagnose but it is important to monitor the UC by checking anemia, as it is one of the symptoms of the disease. It is also done for detecting the presence of infection. Different kinds of blood tests are:
A. Routine Blood Tests
These are done to identify anemia, infection, signs of inflammation, and deficiencies of minerals or vitamins in the body.
B. Antibody Blood Tests
The signs and symptoms of UC and Crohn’s disease are similar and it makes confusion to diagnose the disease. Blood tests for antibodies help to decide, whether it is UC or Crohn’s disease. This test helps to examine the antibodies, proteins generated by the immune system, which give the proper indication of the presence of disease.
3. Stool Sample Test
This test is done to detect the presence of blood in your stool. This is done by taking a stool sample of the patient. The presence of white blood cells (WBCs) in the stool may symbolize ulcerative colitis. This test also helps to detect other GI disorders, such as infections (caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites).
4. Imaging Tests
Ulcerative colitis can also affect the other parts of the body. So, imaging tests provide the images of different parts of the body, which help to identify the condition by showing the areas that are affected and identify possible complications. The commonly recommend imaging tests for ulcerative colitis are:-
A. X-Ray
The conventional X-ray is done to examine the abdominal area to identify serious complications.
B. Colon X-Rays
It is used to detect alterations or abnormalities in the large intestine. It is also known as barium enema because this test examines the intestine by following the movement of viscous, chalky liquid called barium. This liquid coats the lining of the intestine and provides dark shape and outline of the rectum.
C. CT Scan
To diagnose ulcerative colitis doctors also recommend a CT scan because it gives the site and extent of the disease. It generates a cross-sectional picture of the bowel and tissues present outside the bowel.
D. Computerized Tomography Enterography and Magnetic Resonance Enterography
These tests are performed to detect the inflammation in the bowels and are more sensitive than conventional imaging tests.
Also, Read about Ayurvedic Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.




